
Automotive Industry Standards of the People's Republic of China
QC/T993-2015
Explosive transport vehicle
Released on May 30th, 2015 Implemented on October 1st, 2015
Issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China
Table of contents
Preface
1 Scope
2 Normative References
3 Terms and definitions
4 Requirements
5 Test methods
6 Inspection Rules
7 Signs, Identification, and User Manual
8 Accompanying documents, transportation, and storage
Appendix A (normative appendix) Technical requirements and inspection rules for explosion-proof containers
Appendix B (informative appendix) List of names of civilian explosives
Explosive materials loaded with vehicles
Preface
This standard is drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009.
Please note that certain contents of this standard may involve patents, and the issuing authority of the standard does not assume the responsibility of identifying these patents.
This standard is proposed by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China.
This standard is under the jurisdiction of the National Automotive Standardization Technical Committee.
Drafting units of this standard: Zhengzhou Hongyu Special Purpose Vehicle Co., Ltd., Weapon Industry Safety Technology Research Institute, China Weapon Industry Second and Third Research Institute, Shanghai Aviation Special Vehicle Co., Ltd., Jinhua Jiangyouming Carriage Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Zhongtian High tech Special Vehicle Co., Ltd., Shandong Zhengtai Hill Special Purpose Vehicle Co., Ltd., Jiangxi Jiangling Automobile Group Modified Vehicle Co., Ltd Hunan Jinhua Vehicle Co., Ltd., Hunan Futeng He Security and Explosion Prevention Technology Co., Ltd., and Hanyang Special Vehicle Research Institute
The main drafters of this standard are Wang Jianguo, Bai Chunguang, Hou Yonghua, Zhe Enyi, Tu Zhongming, Jiang Youming, Duan Liancheng, Dong Jinhui, Ling Liangxing, Dai Yong, Tang Heping, Yao Hongzhi, Xia Jie, Li Genyun, He Xiaosan, and Wang Dongtang
This standard is issued for the first time.
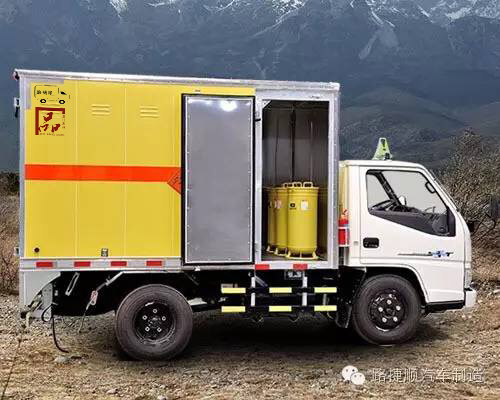

Explosive materials loaded with vehicles
1 Scope
This standard specifies the terms and definitions, requirements, test methods, inspection rules, markings, markings, user manuals, accompanying documents, transportation, storage, and other contents of explosive transport vehicles.
This standard is applicable to explosive transport vehicles (hereinafter referred to as "vehicles") that are modified using a standardized vehicle or a standardized Class II chassis.
2 Normative References
The following documents are essential for the application of this document. For dated references, only the dated version applies to this document. For undated references, the latest version (including all modification orders) applies to this document.
GB 1589 Dimensions, Axle Load, and Mass Limits for Road Vehicle Outlets
GB 4715 point type smoke fire detector
GB 4785 Installation Regulations for External Lighting and Light Signaling Devices of Motor Vehicles and Trailers
GB 6944-2012 Classification and Product Name Numbers of Dangerous Goods
GB 7258 Technical Conditions for Motor Vehicle Operation Safety
GB 8031 Industrial Electric Detonator
GB/T 8162 Seamless Steel Tubes for Structural Purposes
GB/T 9969 General Principles of Industrial Product User Manual
GB 11567.1 Side Protection Requirements for Motor Vehicles and Trailers
GB 11567.2 Requirements for Rear Underbody Protection of Vehicles and Trailers
GB/T12673 Measurement methods for main dimensions of automobiles
GB/T 12674 Automotive Mass (Weight) Parameter Measurement Method
GB 13365 Motor Vehicle Exhaust Spark Extinguishers
GB 13392 Road Transport Dangerous Goods Vehicle Markings
GB/T 13594 Anti lock Braking Performance and Test Methods for Motor Vehicles and Trailers
GB/T 17350 Terminology and Codes for Special Purpose Vehicles and Special Purpose Semi trailers
GB/T 18411 Road Vehicle Product Labels
GB/T 19056 Automotive Travel Recorder
GB20300 Safety Technical Conditions for Road Transport of Explosives and Highly Toxic Chemicals Vehicles
GB 21668 Structural Requirements for Dangerous Goods Transport Vehicles
GB/T 24545 Technical Requirements for Vehicle Speed Limit Systems
GB 25990 Vehicle Rear Sign Plate
GB 50089 Safety Code for Design of Civil Blasting Equipment Engineering
QC/T 252 Type Approval Test Procedure for Special Purpose Vehicles
QC/T 484 Automotive Paint Coatings
QC/T 639 Rubber Sealing Strip for Automobile
JB/T 5943 General Technical Conditions for Welding Parts of Construction Machinery
JT 230 Automotive Static Conductive Rubber Trailer
JT 230 Automotive Static Conductive Rubber Trailer
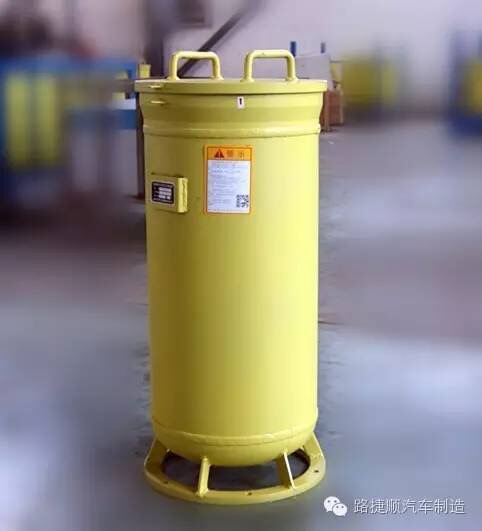

Explosion resistant container
3 Terms and definitions
The terms and definitions established in GB/T17350 and the following apply to this document.
3.1
Explosive transport vehicle
Vehicles transporting explosives. Including civilian explosives transport vehicles, fireworks and firecracker transport vehicles, and explosives co carrier vehicles.
3.2
The vehicle which can transport explosives and explosives at the same time
A special explosive transport vehicle equipped with explosion-proof containers and transporting explosives and detonators simultaneously.
3.3
Anti explosion containers
A container for storing detonators with certain resistance to burst, martyrdom, explosion shock wave, electromagnetic wave shielding, and noise insulation.
3.4
Anti burst performance
The ability of an explosion-proof container to resist rupture caused by the explosion of an inner detonator.
3.5
Anti detonation properties
The ability of an explosion resistant container to prevent adjacent explosive materials from being detonated simultaneously when detonators are installed inside the container.
3.6
Anti shock wave overpressure performance
The ability of the anti explosion container to attenuate shock wave overpressure when the detonator inside the container explodes.
3.7
Shielding effectiveness of anti explosion container
The ratio of the signal value received without an explosion-proof container to the signal value received inside the explosion-proof container, which is the insertion loss caused by the presence of an explosion-proof container in the transmitting and receiving antennas, expressed in dB.
3.8
Fire performance of anti explosion container
The ability of the explosion-proof container to prevent flames from leaking out when the detonator inside the explosion-proof container explodes.
3.9
Anti explosion container deposit dose
The maximum allowable storage capacity of explosion-proof containers (or equivalent to the storage capacity of No. 8 instantaneous industrial electric detonators).
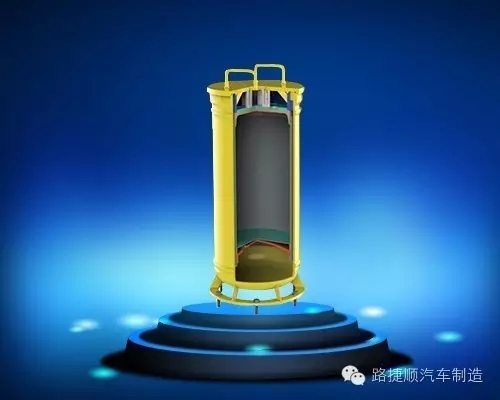

4 Requirements
4.3 Explosive materials loaded with vehicles
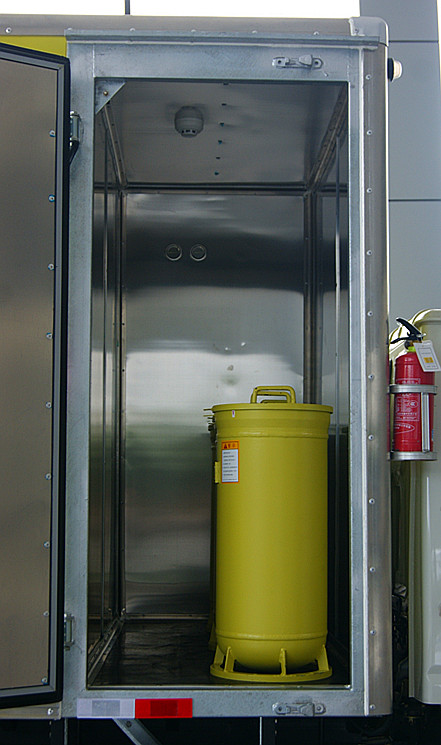
4.3.1 The partition wall separating the cargo compartment into two independent cargo compartments should be equipped with materials that can absorb the energy of explosion shock waves and are non combustible (or flame retardant). The front compartment should have side doors as the passage, and the rear compartment should have rear doors as the passage. One compartment is loaded with explosives not exceeding the specified weight, while the other compartment is loaded with detonators not exceeding the specified quantity. The detonators must be loaded in explosion-proof containers.
4.3.2 When installing explosion-proof containers, the position of the explosion relief hole should avoid being opposite to important components of the car chassis.
4.3.3 Detonators and explosives should be labeled on the inner side of the rear and side doors of the same vehicle, respectively.
4.3.4 The amount of explosives transported by the same vehicle should not exceed 1000kg, and the amount of explosives transported by detonators should not exceed 300g.
4.3.5 The storage capacity of a single explosion-proof container should not exceed 100g (or the equivalent number of No. 8 instantaneous industrial electric detonators should not exceed 100 rounds).
4.3.6 The technical requirements and test methods for explosion-proof containers are shown in Appendix A.
4.3.7 The side wall of the cargo compartment should be equipped with ventilation windows with rainproof function, which should be able to prevent foreign objects from entering.
4.3.8 It is strictly prohibited to install any lighting fixtures and other electrical equipment in the cargo compartment, except for smoke and fire detectors.
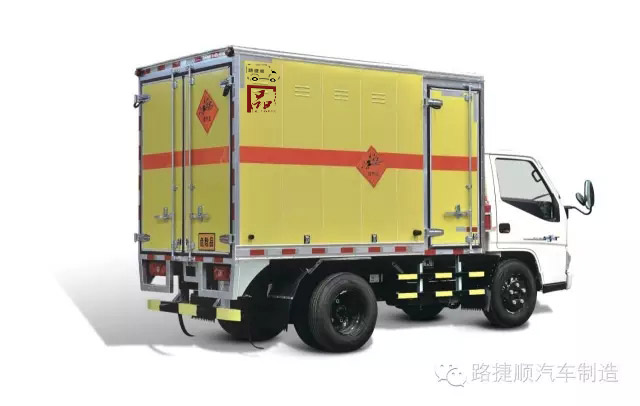

Explosive materials loaded with vehicles
5 Test methods
5.1.1 The measurement of vehicle external dimensions shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T12673, and the measurement of axle load and mass shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB/T12674.
5.1.2 The driving safety related tests of vehicles shall be carried out in accordance with the relevant provisions of GB7258.
5.1.3 The inspection of the external lighting and light signaling devices of the vehicle shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB4785.
5.1.4 The testing of vehicle side and rear lower protection devices shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB 11567.1 and GB 11567.2. Measure the buffer size of the front and rear protective devices.
5.1.5 Visually inspect the installation position of the exhaust pipe and measure the relative position between the exhaust pipe and the fuel tank with a ruler. When the exhaust pipe is installed below the cargo compartment floor, the reliability and effectiveness of installing an insulation board between the exhaust pipe and the cargo compartment floor should be checked.
5.1.6 Check the installation position and quantity of static conductive rubber towing strips.
5.1.7 Check the installation positions of hazard alarm systems, smoke and fire detectors, alarm buzzers, anti-theft alarm systems, and rear video monitoring systems for vehicles transporting civilian explosives, and test their functional effectiveness.
5.1.8 Check the specifications of the tires and the number of dry powder fire extinguishers.
5.1.9 Rainproof sealing test
The carriage door is closed normally. When the rainfall intensity is ≥ 0.12mm/s, a rain gauge should be used to measure the rainfall. The artificial rainfall on the rain test bench should cover the entire carriage. After a 15 minute rain proof sealing performance test, dry the external water accumulation of the carriage, open the car door, and check for water ingress and leakage in all parts of the carriage.
5.1.10 Visually inspect the structure of the cargo compartment, ventilation windows on the side walls of the cargo compartment, rubber products equipped to alleviate cargo collisions, flame retardant and static conductive rubber plates laid, and measure their thickness and dimensions, as well as safety components such as door rubber seals.
5.1.11 Static conductivity test
The interior of the cargo compartment should be clean, and a megohmmeter should be used to measure the resistance between the floor of the cargo compartment and the connection of the towing strip. Measure one point every 2m2 and calculate the average value.
5.1.12 Alarm performance test
Open the rear or side door, check if the alarm device in the driver's cab sounds within 10 seconds, and measure the sound level of the alarm using a noise meter.
5.1.13 Check the structure of the isolation wall, materials inside the interlayer, and the number of explosion-proof containers for explosive materials and vehicles.
6 Inspection Rules
6.1 Factory inspection
6.1.1 Each product should undergo factory inspection, and can only be shipped after passing the inspection by the quality inspection department of the manufacturer and issuing a product certificate.
6.1.2 Factory inspection items:
a) Appearance;
b) Vehicle size and mass parameters;
c) Signs and markings;
d) Installation of external lighting and light signaling devices;
e) Installation dimensions of protective devices;
f) Exhaust pipe installation;
g) Functional inspection of hazard alarm system;
h) Rainproof sealing;
i) Anti theft alarm performance.
6.2 Type inspection
6.2.1 Type inspection should be carried out in one of the following situations:
a) When a new or old product is transferred to another factory for trial production and finalization;
b) Accumulated normal production output of 2000 vehicles;
c) When production resumes after 3 years of product discontinuation;
d) After formal production, if there are significant changes in materials and processes that may affect product performance;
e) When there is a significant difference between the factory inspection and the type inspection.
During the type inspection in 6.2.2, if it falls under the two situations of a) and b) in 6.2.1, the inspection should be carried out in accordance with Chapter 4, QC/T252, and relevant national regulations; If it falls under the condition of c) in 6.2.1, the dedicated performance should be inspected; If it falls under the two situations of d) and e) in 6.2.1, only the affected items can be inspected.

7 Signs, Identification, and User Manual
7.1 Marks and Identification
7.1.1 There should be safety sign graphics and text on the vehicle. Safety signs, signs, and lights should comply with the relevant provisions of GB13392, GB20300, and GB7258.
7.1.2 Product labels should be installed on the vehicle, and the content of the labels should comply with the provisions of GB/T18411 and GB7258.
7.1.3 The side and rear of the vehicle compartment should be equipped with reflective markings and orange reflective tape that can reflect the outline of the cargo compartment, and their requirements should comply with the provisions of GB20300 and GB7258. Vehicles with a total mass greater than or equal to 12000 kg should also be equipped with rear end marker plates that comply with GB25990 regulations.
7.1.4 The inner side of the vehicle's cargo compartment door should be pasted with the "Transportation Table for Civilian Explosives in the Same Vehicle" that meets the storage requirements of hazardous materials in the same warehouse as specified in the GB50089 standard.
7.2 User Manual
The preparation of the vehicle user manual should comply with the provisions of GB/T9969 and GB7258, and should include the following content:
a) Product name and model;
b) Name and detailed address of the production enterprise;
c) Technical characteristics;
d) Structural characteristics;
e) Use and maintenance;
f) Technical maintenance;
g) Emergency response methods;
h) Table for the transportation of civilian explosives on the same vehicle.
8 Accompanying documents, transportation, and storage
8.1 Accompanying documents
The accompanying documents should include:
a) Product qualification certificate and chassis qualification certificate;
b) Product user manual;
c) Car (chassis) user manual;
d) List of accompanying spare parts and accessories.
8.2 Transportation
When vehicles are transported by railway (or waterway), they can get on and off (ships) by self driving (or towing). If lifting is necessary for loading and unloading, special lifting tools must be used to prevent damage to the product.
8.3 Storage
When the vehicle is parked for a long time, the coolant and fuel should be drained, the power should be cut off, the doors and windows should be locked, and placed in a ventilated, moisture-proof, and fire-fighting area. Regular maintenance should be carried out according to the product manual.
Appendix A
(Normative Appendix)
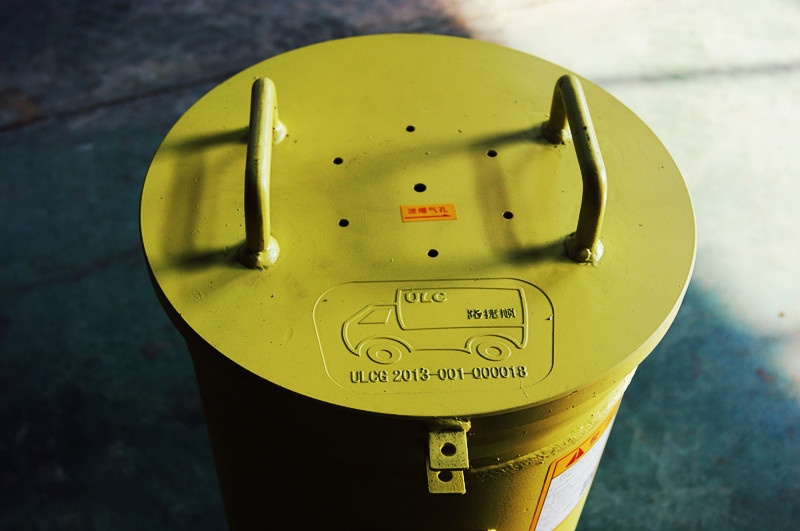
Technical requirements and inspection rules for explosion-proof containers
A. 1 Technical Requirements
A. 1.1 Rated loading capacity
The maximum allowable loading capacity of explosion-proof containers: TNT equivalent of detonators ≤ 100g (or ≤ 100 instantaneous industrial electric detonators conforming to GB8031);
A. 1.2 Materials
The materials used for explosion-proof containers should be able to withstand considerable pressure without causing rupture, and their performance indicators should comply with the provisions of GB/T8162.
A. 1.3 Appearance quality
The appearance should be free of paint peeling, bumps, flash edges, and burrs.
A. 1.4 Painting
A. 1.4.1 The interior and exterior of the explosion-proof container body should be coated with anti rust paint. Except for the explosion relief hole area, the other exposed surfaces should be coated with "medium yellow" warning color paint.
A. 1.4.2 Apply black paint on the surface of the vent hole.
A. 1.4.3 The paint coating should comply with the provisions of QC/T484.
A. 1.5 Structure
A. 1.5.1 Safety relief holes should be installed in the structural design.
A. 1.5.2 The venting hole and the storage room of the explosion-proof container are separated by aluminum foil rupture discs.
A. 1.5.3 Except for explosion relief holes, all other structures should be double layered.
A. 1.6 Welding parts
Weldments should comply with the relevant provisions of JB/T 5943.
A. 1.7 Safety factor
The explosion-proof safety factor of explosion-proof containers should not be less than 200%.

A. 1.8 Performance
A. 1.8.1 Explosion resistance performance
The explosion-proof container is equipped with detonators with a maximum allowable storage capacity of twice the quantity. When an explosion occurs, the explosion-proof container body should not be damaged except for the leakage hole, but other parts should not be damaged by explosion, but deformation is allowed.
A. 1.8.2 Anti explosion performance
The explosion-proof container contains detonators with a maximum allowable storage capacity of twice the quantity. When an explosion occurs, the explosion-proof container can prevent other nearby civilian explosives from being detonated simultaneously.
A. 1.8.3 Resistance to shock wave overpressure
The maximum allowable storage quantity of explosives inside the explosion-proof container is detonator. When an explosion occurs, the overpressure of the shock wave at a distance of 2.5m outside the side of the explosion-proof container should not exceed 0.02 MPa.
A. 1.8.4 Shielding effectiveness of explosion-proof containers
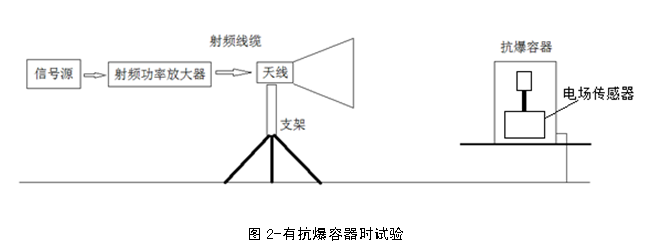
Anti explosion containers should have certain shielding performance against electromagnetic waves. When it is in the electromagnetic wave field within the frequency range of 30MHz-3GHz, the explosion-proof container should have a shielding efficiency of more than 20dB.
A. 1.8.5 Fire performance
The maximum allowable quantity of explosive stored in the explosion-proof container is detonator, and when an explosion occurs, there should be no visual flame.
A. 1.8.6 Noise isolation
The maximum allowable quantity of explosives stored inside the explosion-proof container is detonator. When an explosion occurs, the noise at a distance of 5 meters outside the side of the explosion-proof container should not exceed 115 dB.
A. 2 Test methods
A. 2.1 Test conditions
A. 2.1.1 Types of civilian explosives for testing
No. 8 instantaneous industrial electric detonator in accordance with GB8031;
A. 2.1.2 Test site
An explosion testing site recognized by relevant national departments.
A. 2.3 Test methods
The anti explosion container is installed on a frame similar to the chassis of a vehicle, and the anti explosion container is securely fixed by simulating the explosive substance being loaded with the vehicle. The following tests are conducted.
A. 2.3.1 Burst resistance test
The explosion-proof container is equipped with double the designed explosive storage capacity of detonators (200 No. 8 instant industrial electric detonators in accordance with GB8031 regulations), which are artificially detonated and the anti explosion performance of the explosion-proof container after testing is checked.
A. 2.3.2 Explosion resistance test
The explosion-proof container is designed to store twice the quantity of detonators (such as 200 instantaneous industrial electric detonators in accordance with GB8031), and 100 detonators that are the same as those inside the container are tied on the outer wall of the explosion-proof container to artificially detonate the detonators inside the explosion-proof container. Check the resistance of detonators tied on the outer wall of the anti explosion container after the test.
A. 2.3.3 Shock wave overpressure resistance test
The explosion resistant container is equipped with a corresponding number of detonators (100 sets of No. 8 instantaneous industrial electric detonators in accordance with GB8031 regulations), and four sets of impulse wave overpressure sensors are evenly distributed at a circumference of 2.5m horizontally from the center of the explosion resistant container. The detonators inside the explosion resistant container are artificially detonated.
A. 2.3.4 Shielding effectiveness test
a) Technical requirements for using equipment:
b) Coverage frequency range: 30MHz-3GHz;
c) Test distance between antenna and explosion-proof container: 0.5m-1m;
d) The polarization mode of the antenna: vertical polarization, horizontal polarization.
e) Test steps:
① Connect all instruments and equipment and check the connection status;
② The distance between the fixed antenna and the electric field sensor;
③ Warm up all instruments and equipment for 30 minutes;
④ When there is no explosion-proof container, measure the intensity of the electromagnetic field emitted by the antenna at the fixed point. Record all measurement data, which can be represented by E1.
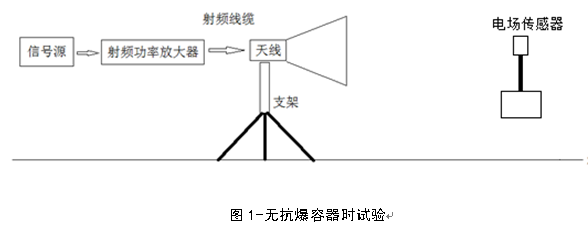
⑤ When loading the anti explosion container, place the electric field sensor inside the anti explosion container and seal it to measure the response of the antenna radiated electromagnetic field inside the anti explosion container. When there is an explosion-proof container, the electric field intensity measured by the electric field sensor is recorded, which can be represented by E2.
⑥ Test data statistics
Using formula:
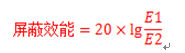
Finally, the corresponding relationship between the shielding effectiveness and frequency of the explosion-proof container is obtained, and the results are represented by the response curve between frequency and shielding effectiveness.
⑦ Shielding effectiveness test report
This should include the instruments and equipment used, the calibration of their measurement, testing arrangements, measurement results, shielding effectiveness curves, etc.
A. 2.3.5 Fire performance test
Install a corresponding number of detonators with the designed storage capacity in the explosion-proof container fixed in the carriage, manually detonate, and visually inspect.
A. 2.3.6 Noise isolation test
The explosion resistant container is equipped with a corresponding number of detonators (100 No. 8 instantaneous industrial electric detonators in accordance with GB8031 regulations), which are artificially detonated. The noise value is measured using a sound level meter at a horizontal distance of 5m from the center of the explosion resistant container.
A. 3 Inspection Rules
A. 3.1 Factory inspection
A. 3.1.1 The product should undergo 100% factory inspection, and can only leave the factory after passing the inspection by the quality inspection department of the manufacturer and issuing a product certificate.
A. 3.1.2 Factory inspection items:
a) Appearance quality;
b) Painting;
c) Welding.
A. 3.1.3 Judgment rules
The inspected product must pass all factory inspection items. When there are two unqualified items, rework is allowed once. If the product still fails after re inspection after rework, it should be determined as unqualified.
A. 3.2 Type inspection
A. 3.2.1 Type inspection shall be conducted in any of the following cases:
a) When a new or old product is transferred to another factory for trial production and finalization;
b) When production resumes after two years of production suspension;
c) Accumulated normal production output of 2000 units per hour;
d) After formal production, if there are significant changes in materials and processes that may affect product performance;
e) When there is a significant difference between the factory inspection and the type inspection.
A. 3.2.2 Type inspection items:

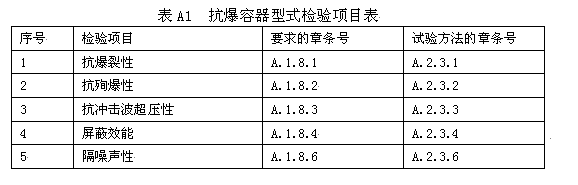
A. 3.2.3 Sampling quantity
Extract 3 units from batch products.
A. 3.2.4 Qualification criteria
The tested product must pass all the type inspection items specified in this standard. Any non conformance shall be deemed as product non conformance.
A. 4 Signs
A. 4.1 The surface of explosion-proof containers should be sprayed with "model", "name" and warning signs.
A. 4.2 Explosion resistant containers should have product labels, which should include the following content:
a) Product name and model;
b) Main technical parameters: TNT equivalent of detonator XXX g or XXX detonator;
c) Factory number and production date;
d) Name of the manufacturer.

